Reconnaissance tools are used to collect basic information about target systems to exploit them. Information collected by the footprinting tools includes the target’s IP location information, routing information, business information, address, phone number and social security number, details about a source of an email and a file, DNS information, domain information, and so on.
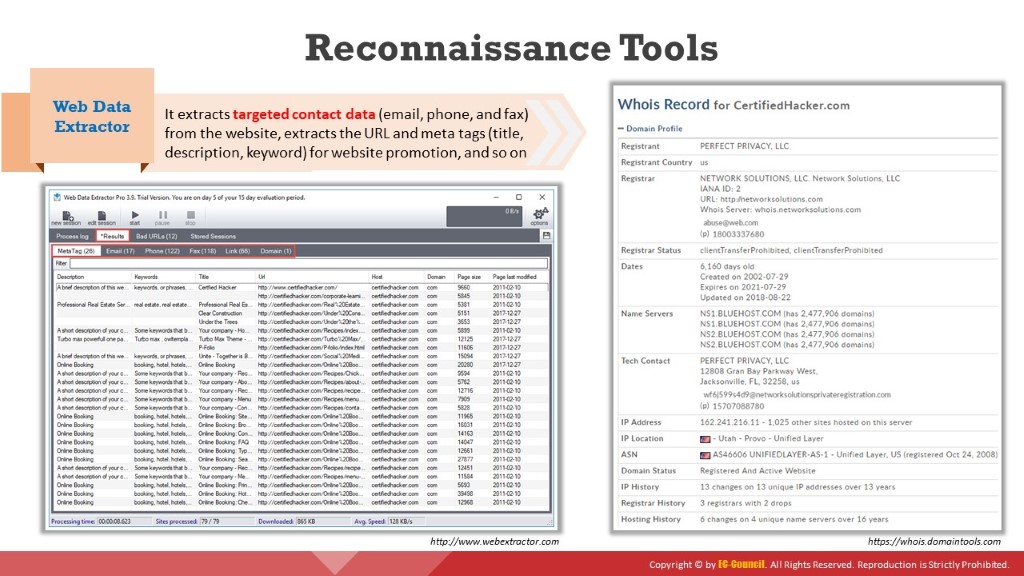
Web Data Extractor
Source: http://www.webextractor.com
Web Data Extractor automatically extracts specific information from web pages. It extracts targeted contact data (email, phone, and fax) from the website, extracts the URL and meta tags (title, description, keyword) for website promotion, searches directory creation, performs web research, and so on.
As shown in the screenshot, attackers use Web Data Extractor to automatically gather critical information such as lists of meta tags, e-mail addresses, and phone and fax numbers from the target website.
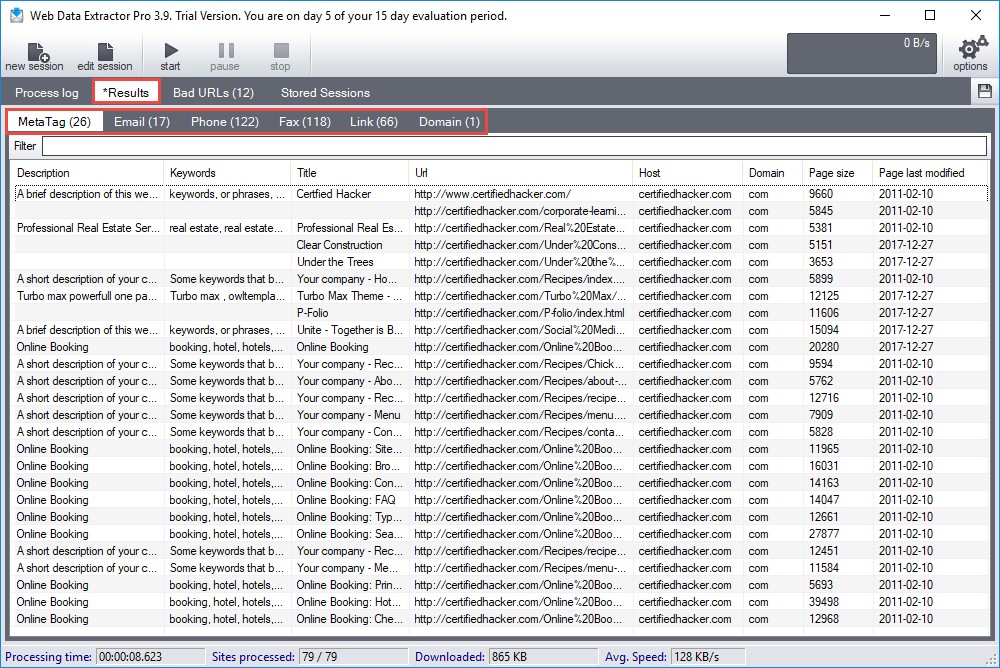
Figure 2.3: Screenshot of Web Data Extractor
Whois Lookup
Whois services such as https://whois.domaintools.com or https://www.tamos.com can help to perform Whois lookups. The screenshot shows the result analysis of a Whois lookup obtained with the two above-mentioned Whois services. The services perform Whois lookup by entering the target's domain or IP address. The domaintools.com service provides Whois information such as registrant information, email, administrative contact information, creation and expiry date, and a list of domain servers. SmartWhois, available at http://www.tamos.com, gives information about an IP address, hostname, or domain, including information about the country, state or province, city, phone number, fax number, name of the network provider, administrator, and technical support contact information. It also helps in finding the owner of the domain, the owner's contact information, the owner of the IP address block, registered date of the domain, and so on. It supports Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs), which means one can query domain names that use non-English characters. It also supports IPv6 addresses.

Figure 2.4: Screenshot of WhoIs
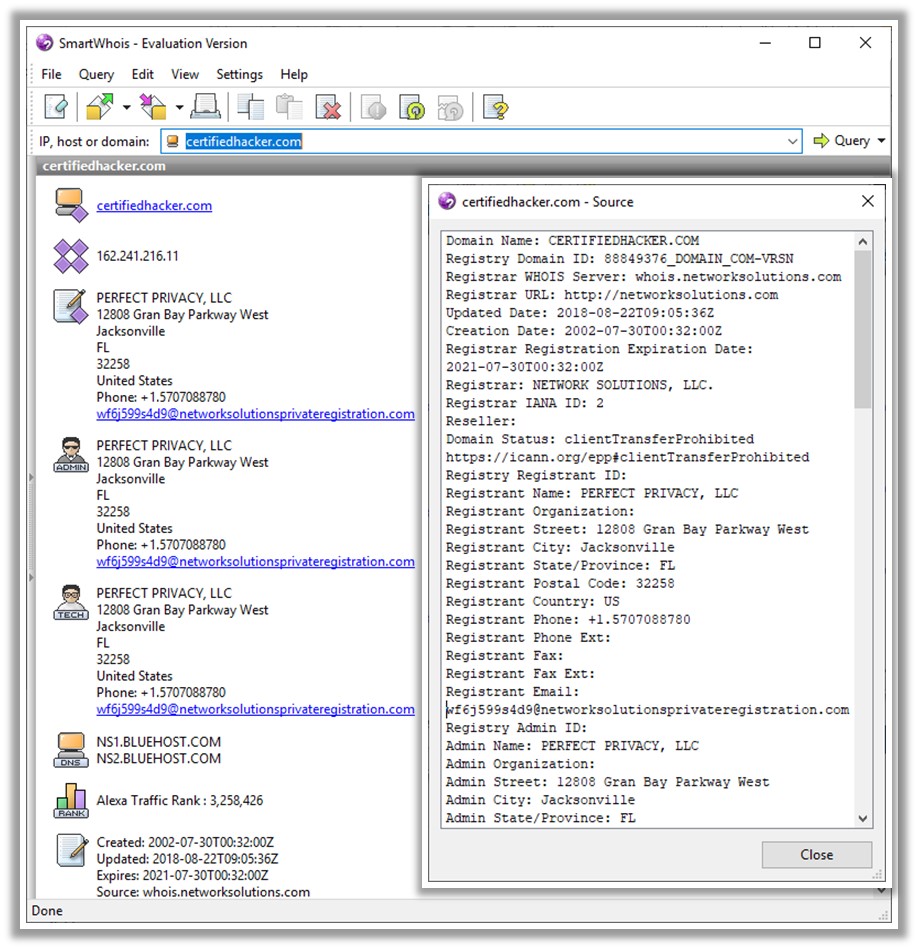
Figure 2.5: Screenshot of SmartWhois
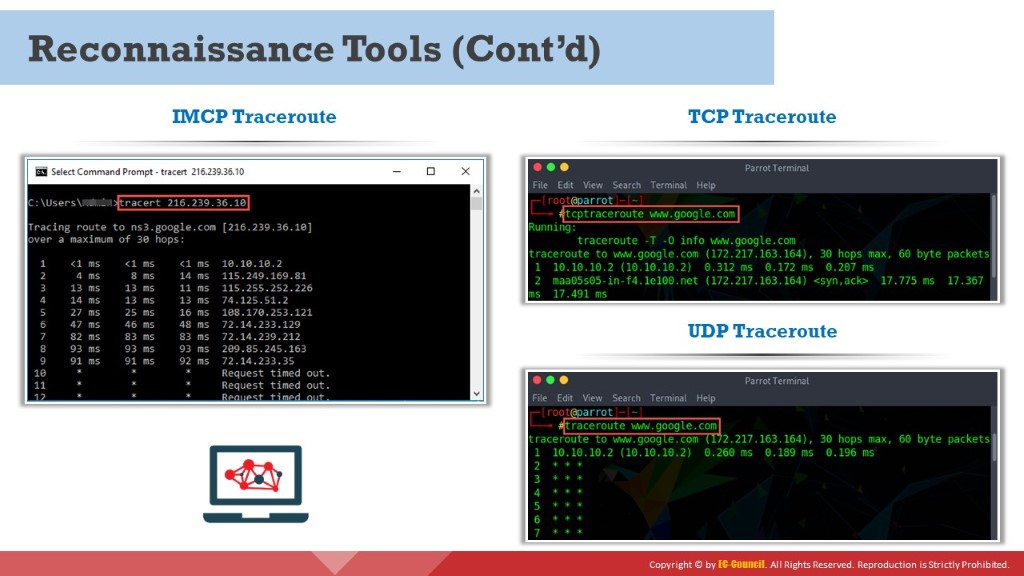
ICMP Traceroute
Windows operating system by default uses ICMP traceroute. Go to the command prompt and type the tracert command along with the destination IP address or domain name as follows:
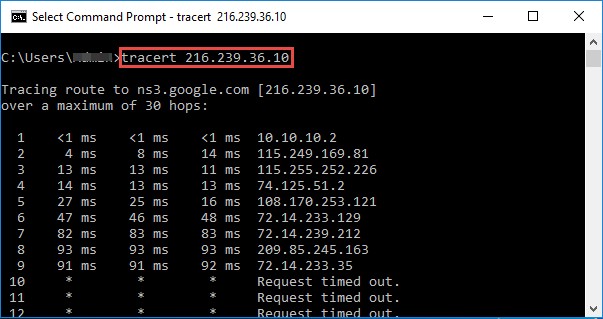
Figure 2.6: Screenshot showing the output of ICMP Traceroute
TCP Traceroute
Many devices in any network are generally configured to block ICMP traceroute messages. In this scenario, an attacker uses TCP or UDP traceroute, which is also known as Layer 4 traceroute. Go to the terminal in Linux operating system and type the tcptraceroute command along with the destination IP address or domain name as follows:
tcptraceroute www.google.com
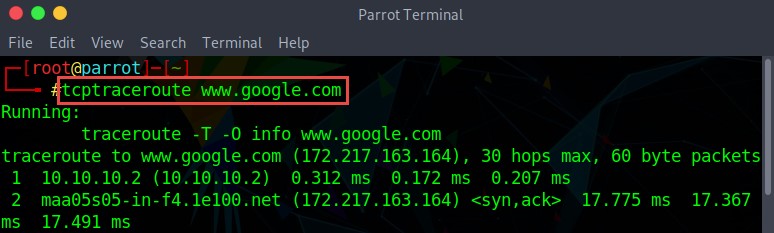
Figure 2.7: Screenshot showing the output of TCP Traceroute
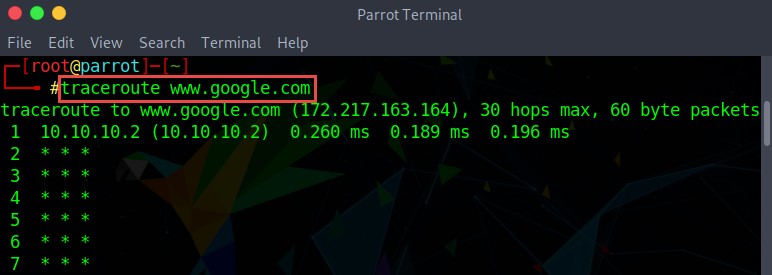
UDP Traceroute
Like Windows, Linux also has a built-in traceroute utility, but it uses the UDP protocol for tracing the route to the destination. Go to the terminal in the Linux operating system and type the traceroute command along with the destination IP address or domain name as follows:
traceroute www.google.com