
-
-
- Ping Method
-
To detect a sniffer on a network, identify the system on the network running in promiscuous mode. The ping method is useful in detecting a system that runs in promiscuous mode, which in turn helps to detect sniffers installed on the network.
Just send a ping request to the suspected machine with its IP address and incorrect MAC address. The Ethernet adapter will reject it because the MAC address does not match, whereas the suspect machine running the sniffer responds to it, as it does not reject packets with a different MAC address. Thus, this response will identify the sniffer in the network.

Figure 6.19: Promiscuous mode

Figure 6.20: Non-promiscuous mode
-
-
- DNS Method
-
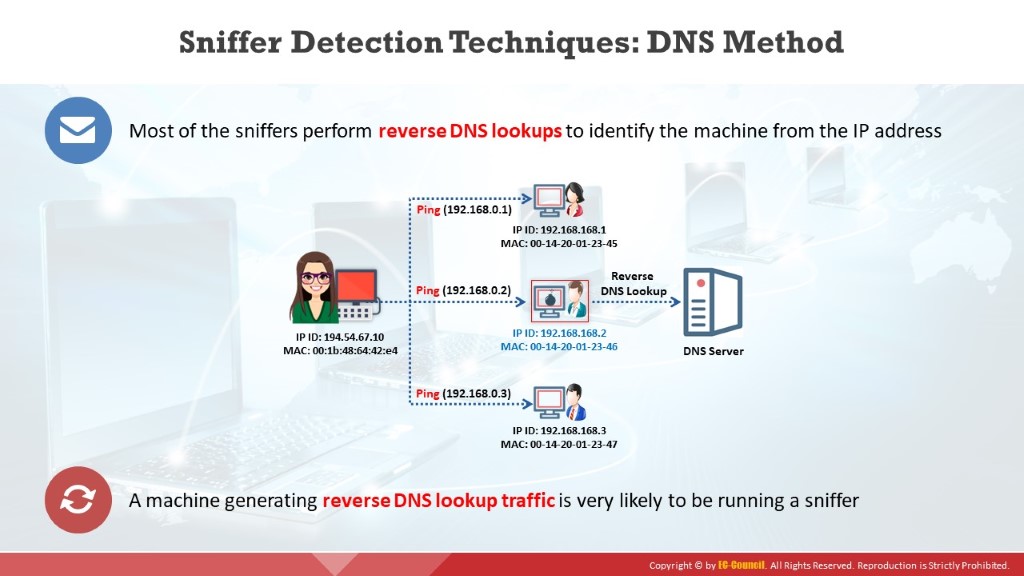
The reverse DNS lookup is the opposite of the DNS lookup method. Sniffers using reverse DNS lookup increase network traffic. This increase in network traffic can be an indication of the presence of a sniffer on the network. The computers on this network are in promiscuous mode.
Users can perform a reverse DNS lookup remotely or locally. Monitor the organization’s DNS server to identify incoming reverse DNS lookups. The method of sending ICMP requests to a non-existing IP address can also monitor reverse DNS lookups. The computer performing the reverse DNS lookup would respond to the ping, thus identifying it as hosting a sniffer.
For local reverse DNS lookups, configure the detector in promiscuous mode. Send an ICMP request to a non-existing IP address and view the response. If the system receives a response, the user can identify the responding machine as performing reverse DNS lookups on the local machine. A machine generating reverse DNS lookup traffic will most likely be running a sniffer.
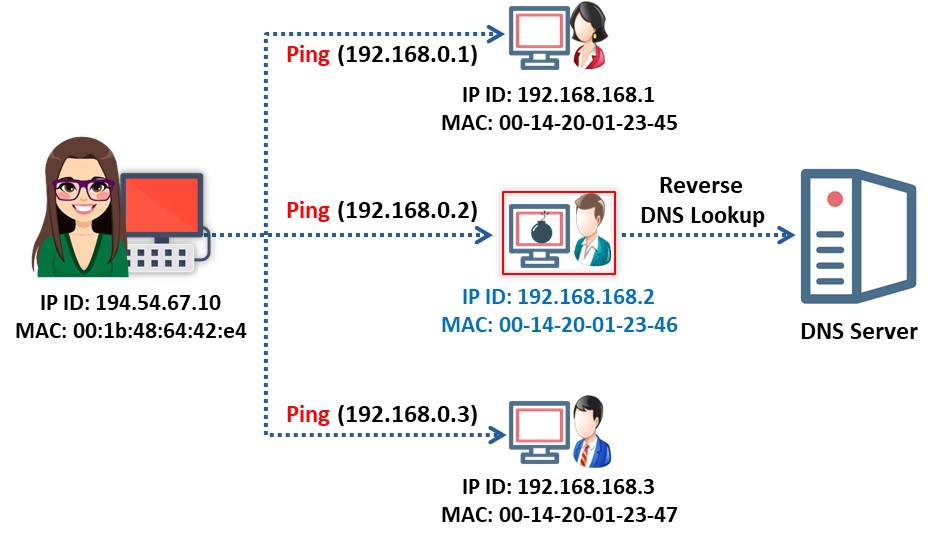
Figure 6.21: Sniffing detection using the DNS method
-
-
- ARP Method
-
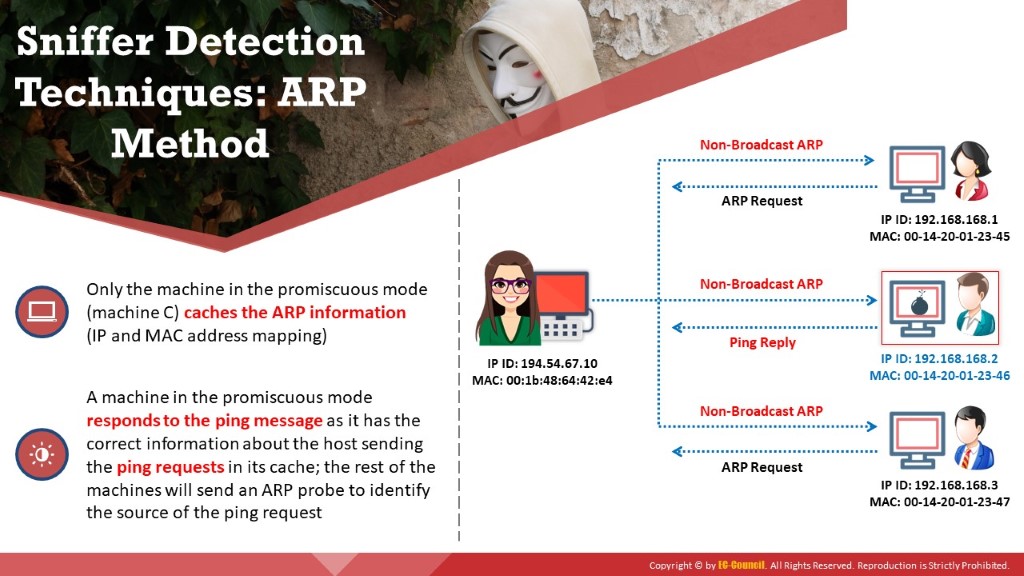
This technique sends a non-broadcast ARP to all the nodes in the network. The node that runs in promiscuous mode on the network will cache the local ARP address. Then, it will broadcast a ping message on the network with the local IP address but a different MAC address. In this case, only the node that has the MAC address (cached earlier) will be able to respond to your broadcast ping request. A machine in promiscuous mode replies to the ping message, as it has the correct information about the host that is sending ping requests in its cache; the remaining machines will send an ARP probe to identify the source of the ping request. This will detect the node on which the sniffer is running.

Figure 6.22: Detecting sniffing via the ARP method